Molecular Science and Engineering at Liquid-Liquid Interfaces: Unveiling the Nanoworld

Delve into the captivating realm of molecular science and engineering at liquid-liquid interfaces, where a myriad of nanostructures emerge, paving the way for groundbreaking applications. This article offers an in-depth exploration of this intriguing field, highlighting its fundamental principles, cutting-edge advancements, and potential implications across diverse disciplines.
Liquid-Liquid Interfaces: A Unique Environment
Liquid-liquid interfaces, where two immiscible liquids meet, exhibit unique properties distinct from the bulk phases. The interfacial region, often just a few nanometers thick, becomes an arena where molecules assemble and organize in fascinating ways, giving rise to a plethora of nanostructures.
4.3 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 5715 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 335 pages |
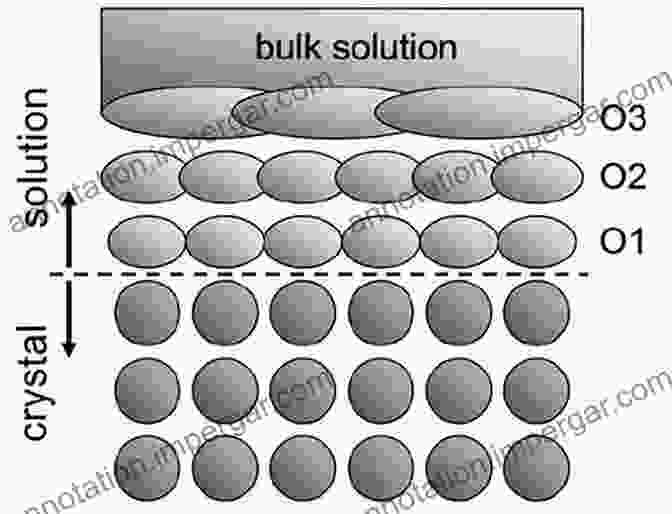
Nanostructure Formation and Control
At liquid-liquid interfaces, the interplay of intermolecular forces, such as van der Waals interactions and electrostatic repulsion, drives the self-assembly of molecules into diverse nanostructures. These structures can adopt various geometries, including spheres, rods, tubes, and more complex shapes.
By manipulating the chemical composition and physical properties of the liquids, scientists can precisely control the formation of these nanostructures, tailoring their size, shape, and arrangement. This exquisite control over nanostructure assembly offers immense potential for designing materials with tailored properties.
Applications in Materials Science
The ability to create and manipulate nanostructures at liquid-liquid interfaces opens up a wide range of applications in materials science. These nanostructures can serve as building blocks for functional materials with unique optical, electrical, and magnetic properties.
For instance, researchers have developed self-assembled nanostructures at liquid-liquid interfaces to create photonic crystals, which control the flow of light in a precise manner. These materials hold promise for applications in optical communications, sensors, and displays.
Additionally, liquid-liquid interfacial engineering has enabled the synthesis of novel nanomaterials with enhanced mechanical properties. These materials exhibit improved strength, toughness, and wear resistance, making them suitable for applications in aerospace, automotive, and biomedical fields.
Advances in Energy and Catalysis
Liquid-liquid interfaces also play a crucial role in energy conversion and catalysis. The unique properties of these interfaces facilitate efficient charge transfer and mass transport, making them ideal platforms for designing novel energy storage and conversion devices.
Researchers have exploited liquid-liquid interfaces to create self-assembled nanostructures that enhance the performance of solar cells and batteries. These nanostructures improve light absorption, charge separation, and ion transport, leading to increased energy conversion efficiency.
Furthermore, liquid-liquid interfacial engineering has enabled the development of highly active and selective catalysts. These catalysts facilitate chemical reactions with increased efficiency and specificity, offering potential applications in sustainable chemical synthesis and environmental remediation.
Biomedical Applications
The field of molecular science and engineering at liquid-liquid interfaces has significant implications in the biomedical realm. Nanostructures formed at these interfaces can serve as drug delivery vehicles, biosensors, and tissue engineering scaffolds.
Self-assembled nanostructures can encapsulate drugs and deliver them specifically to target sites, improving drug efficacy and reducing side effects. Liquid-liquid interfacial engineering also enables the design of ultrasensitive biosensors for detecting biomarkers associated with diseases, facilitating early diagnosis and personalized medicine.
Additionally, liquid-liquid interfaces provide a platform for creating biocompatible nanostructures that mimic the natural extracellular matrix. These nanostructures can support cell growth and differentiation, promoting tissue regeneration and repair.
Molecular science and engineering at liquid-liquid interfaces is rapidly evolving, offering a transformative approach to creating and manipulating nanostructures with tailored properties. The ability to control nanostructure formation opens up endless possibilities for innovation in materials science, energy, catalysis, and biomedicine.
As research in this field continues to advance, we can expect even more groundbreaking discoveries and applications that will shape the future of technology and human well-being.
4.3 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 5715 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 335 pages |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Book
Book Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Reader
Reader Library
Library Paperback
Paperback E-book
E-book Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Paragraph
Paragraph Sentence
Sentence Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Bibliography
Bibliography Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Scroll
Scroll Codex
Codex Tome
Tome Bestseller
Bestseller Classics
Classics Library card
Library card Narrative
Narrative Biography
Biography Autobiography
Autobiography Memoir
Memoir Reference
Reference Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia Gill Bridgewater
Gill Bridgewater Dave Roach
Dave Roach Sarah Paul
Sarah Paul David Kent
David Kent Frank M Pawlak
Frank M Pawlak David Leatherbarrow
David Leatherbarrow David Hillel Ruben
David Hillel Ruben David A Weintraub
David A Weintraub Rodney Gilmour
Rodney Gilmour Darick Robertson
Darick Robertson Gustavo Kaercher Loureiro
Gustavo Kaercher Loureiro Tharran E Gaines
Tharran E Gaines Mage Gate
Mage Gate David Alan Sklansky
David Alan Sklansky Daniel James Hollins
Daniel James Hollins Efstratios Nikolaidis
Efstratios Nikolaidis Recipe Junkies
Recipe Junkies Danni Andrew
Danni Andrew Richard Doherty
Richard Doherty Mike Resnick
Mike Resnick
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Raymond ChandlerDiscover the Intricacies of Pumps and Hydraulic Rams with Paul Hasluck's...
Raymond ChandlerDiscover the Intricacies of Pumps and Hydraulic Rams with Paul Hasluck's... Clark BellFollow ·7.1k
Clark BellFollow ·7.1k George Bernard ShawFollow ·11.5k
George Bernard ShawFollow ·11.5k Colt SimmonsFollow ·2.1k
Colt SimmonsFollow ·2.1k Dylan MitchellFollow ·13.1k
Dylan MitchellFollow ·13.1k Jonathan HayesFollow ·3.7k
Jonathan HayesFollow ·3.7k Hamilton BellFollow ·3.4k
Hamilton BellFollow ·3.4k Brent FosterFollow ·19.7k
Brent FosterFollow ·19.7k Jesus MitchellFollow ·19.7k
Jesus MitchellFollow ·19.7k

 Phil Foster
Phil FosterBuild Your Own 12 Tray Fodder System: Half Pint Homestead...
Are you ready...

 Curtis Stewart
Curtis StewartUnleash the Power of Evolutionary Psychology: Embark on a...
Embark on an...

 Voltaire
VoltaireExcel Scientific and Engineering Cookbook: The Ultimate...
Working in science and engineering often...

 Alan Turner
Alan TurnerGroup Theory and Chemistry: Unveiling the Symmetry and...
In the realm of...
4.3 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 5715 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
| Print length | : | 335 pages |